Introduction
Generative AI has rapidly evolved from a tech curiosity to a transformative force across industries. With the ability to create content, simulate scenarios, and interpret complex data inputs, GenAI enables businesses to unlock new levels of efficiency, creativity, and personalization. Its impact is being felt in boardrooms, back offices, hospitals, classrooms, and factories alike. GenAI’s versatility makes it especially powerful: it can serve the needs of marketing teams creating content, legal departments drafting contracts, and data scientists generating synthetic datasets for modeling.

Furthermore, as organizations strive to do more with less, automating previously manual, repetitive tasks without compromising on quality is critical. Generative AI sits at this intersection of automation and augmentation, enhancing human capabilities while reducing operational overhead. With its dynamic capabilities and adaptive learning mechanisms, it’s positioned as a tool and a strategic enabler across business domains.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence models, such as large language models (LLMs), generative adversarial networks (GANs), and diffusion models, that can generate new content, including text, images, audio, and even code. Unlike predictive models that analyze existing data to forecast outcomes, generative models create entirely new artifacts, often indistinguishable from human-generated content.
These models work by learning from vast amounts of data to understand patterns, styles, and context. For example, a generative text model trained in medical literature can write clinical summaries or health-related FAQs. An image generation model trained on architectural blueprints can design building concepts. Importantly, generative AI does not replicate existing data; rather, it creates novel outputs that align with the learned patterns.
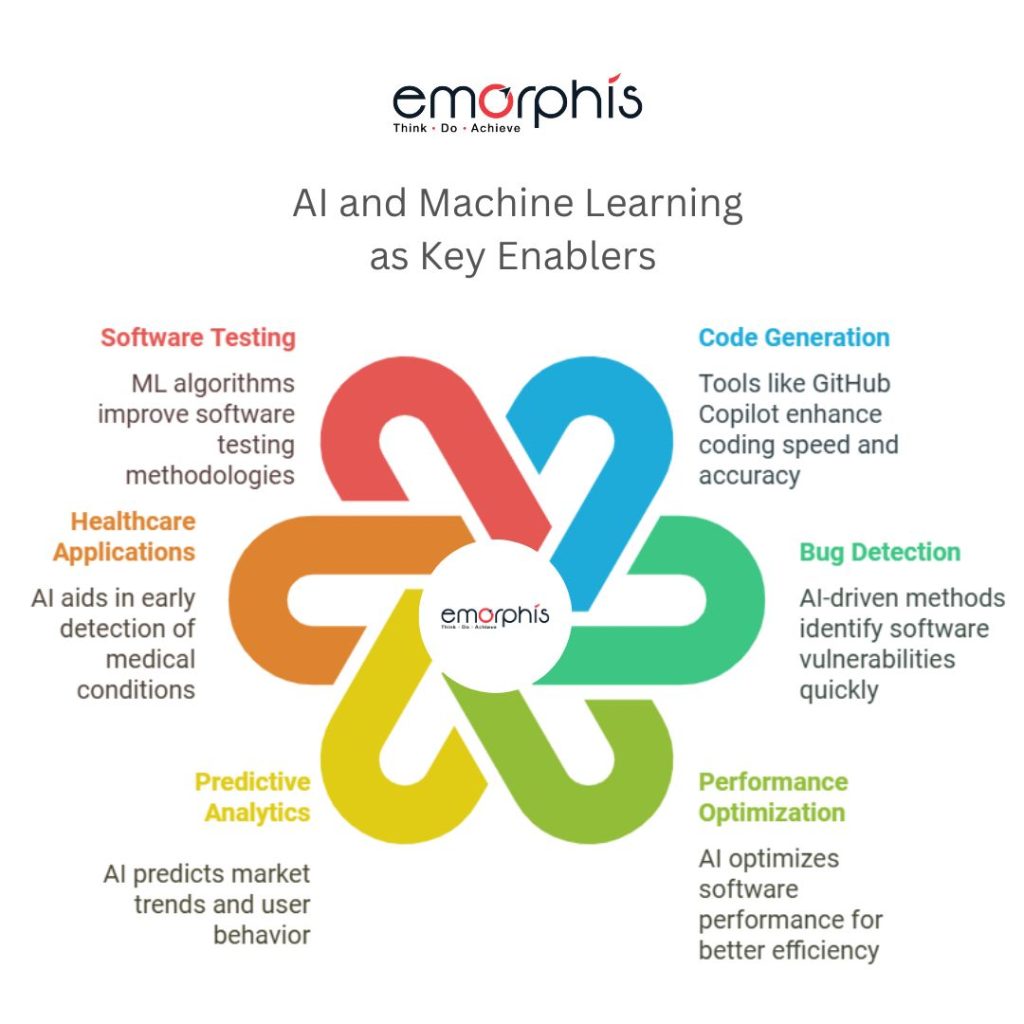
The advent of transformer-based architectures, particularly models like GPT and BERT, has significantly accelerated generative AI’s capabilities. These models are context-aware, scalable, and can be fine-tuned for industry-specific use. As enterprises race to innovate, generative AI emerges as the technology that bridges the gap between massive data repositories and meaningful, real-time output.
Top 5 Cross-Industry Generative AI Use Cases
Generative AI has the flexibility to be applied across various sectors, solving both common and unique challenges. A few core use cases include:
1. Automating Documentation and Content Creation
From legal contracts to HR onboarding manuals and marketing copy, generative AI can generate complex, structured content in minutes. This significantly reduces manual effort while improving consistency and quality. Teams can save hundreds of hours typically spent on drafting and editing. In healthcare, for example, discharge summaries or SOAP notes can be auto-generated based on clinical data.
2. Personalizing Communication at Scale
Businesses often struggle to scale 1:1 interactions with their audience. GenAI allows for personalized outreach, such as email campaigns, chatbot responses, and customer onboarding instructions without needing an army of writers. It tailors content based on customer behavior, demographics, and preferences, driving higher engagement and conversion rates.
3. Interpreting and Summarizing Unstructured Data
Businesses generate and collect massive amounts of unstructured data think emails, PDFs, handwritten notes, or voice transcripts. GenAI can analyze and summarize this data into actionable insights. For instance, in legal practice, it can summarize hundreds of pages of case documents into concise briefs.
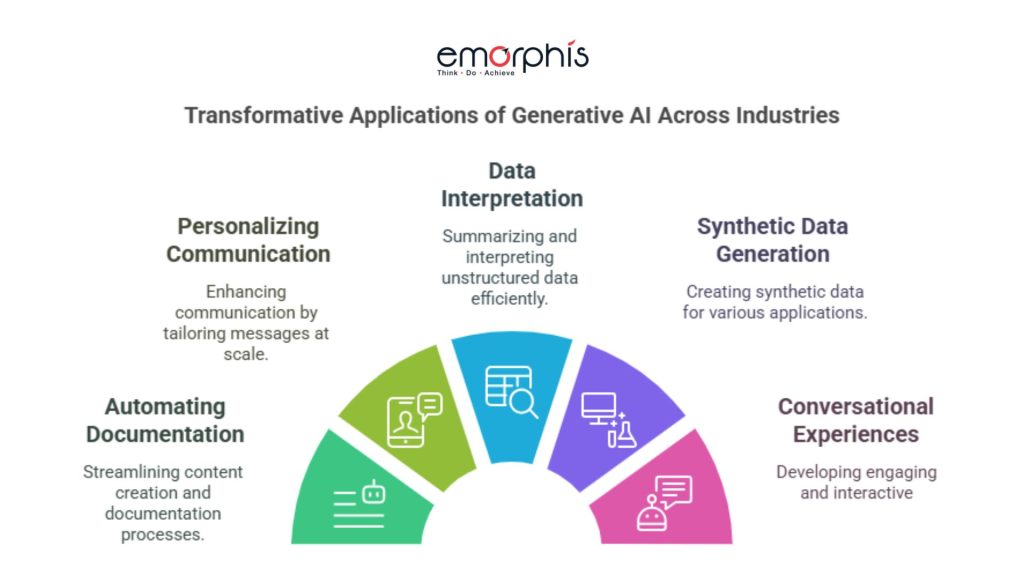
4. Generating Synthetic Data
In industries like healthcare, finance, or automotive, access to quality, annotated data is often limited by regulations or scarcity. GenAI can produce synthetic but statistically similar datasets that help in training AI models, testing systems, or simulating scenarios. These synthetic datasets maintain data privacy while supporting robust development.
5. Creating Conversational Experiences
AI-powered virtual agents can now go beyond FAQs. They can interact, troubleshoot, and offer intelligent recommendations in natural language. This transforms customer service from reactive to proactive, improving satisfaction and reducing call center loads.
Each of these use cases underscores the transformative potential of GenAI to enhance operational efficiency, improve user experiences, and open new revenue opportunities.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
While generative AI offers broad capabilities that transcend industries, its true potential is unlocked when tailored to the unique workflows, regulations, and customer expectations of specific sectors. From automating clinical documentation in healthcare to drafting contracts in legal, GenAI is reshaping how organizations operate and deliver value. Each industry faces distinct challenges, be it fragmented data sources, the need for personalization at scale, or compliance-heavy processes.
Generative AI not only addresses these challenges but also introduces innovative ways to enhance decision-making, streamline operations, and drive better outcomes. In this section, we explore how GenAI is being deployed across major industries including healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, education, and legal.
Each use case showcases how generative models are reimagining core tasks, such as writing, summarizing, recommending, or generating synthetic data, and the tangible benefits they bring in terms of speed, accuracy, and scalability.
Healthcare
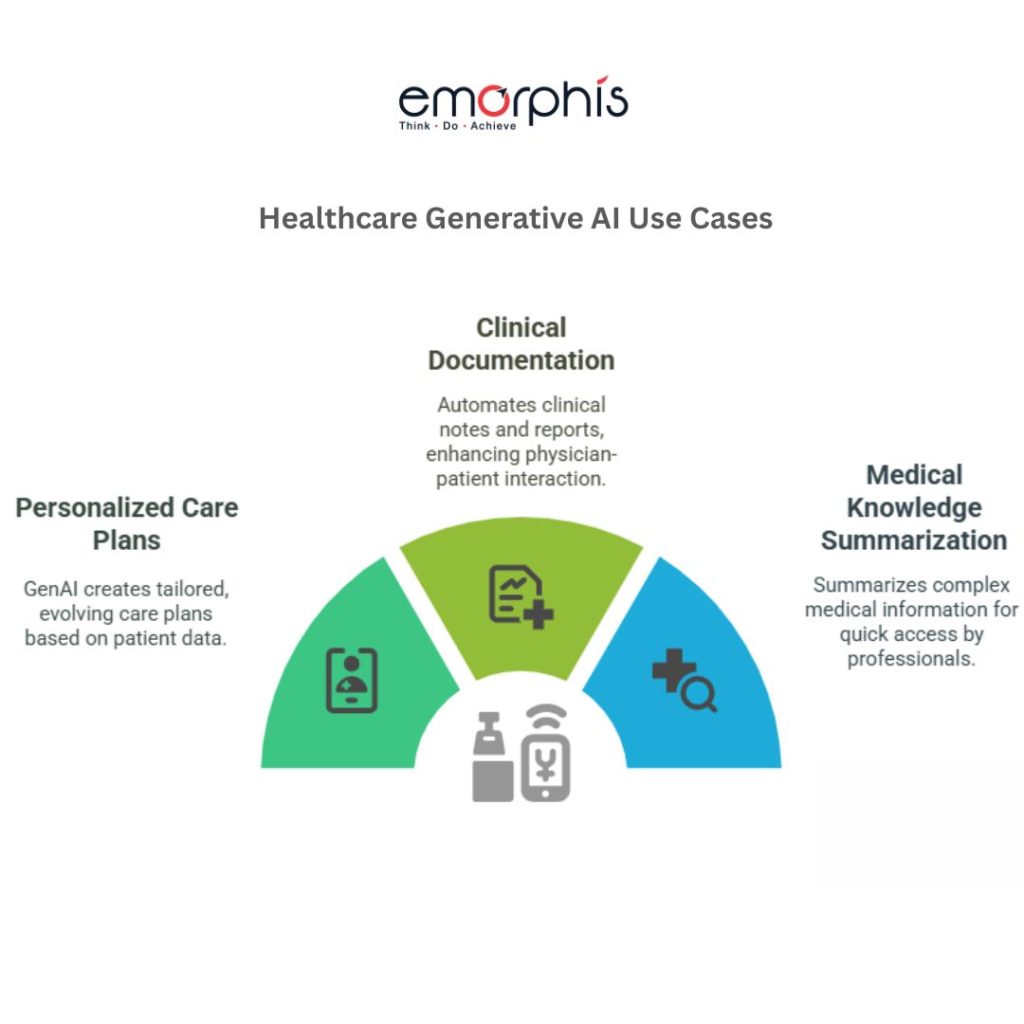
- Personalized Care Plan Generation: GenAI crafts tailored care plans by analyzing patient records, health assessments, medications, and clinical guidelines. These dynamic plans evolve with the patient’s condition and are rooted in transparency and evidence-based practices.
- Clinical Documentation Automation: Automates the creation of clinical notes, discharge summaries, and diagnostic reports, reducing time spent on paperwork and increasing physician-patient interaction.
- Medical Knowledge Summarization: Summarizes medical journals, clinical trial results, and treatment guidelines into digestible formats for clinicians, researchers, and even patients, accelerating access to relevant knowledge.
Finance

- Automated Report Writing and Summarization: Generates earnings reports, investment summaries, and risk analysis documents from financial data, improving turnaround time and accuracy.
- Fraud Scenario Simulation: Creates realistic, synthetic fraud patterns to train detection algorithms, helping financial institutions stay ahead of evolving threats.
- Personalized Investment Advisory: Analyzes investor profiles, market trends, and goals to generate tailored financial plans and product recommendations.
Retail and E-Commerce

- AI-Generated Product Descriptions & Visuals: Creates engaging, SEO-optimized product content and visuals, saving time and enhancing catalog quality across thousands of SKUs.
- Personalized Shopping Assistants: Conversational AI tools guide customers through product selection, addressing queries in real-time and boosting conversion rates.
- Demand Forecasting Content: Uses GenAI to simulate different sales scenarios and provide content tailored to stock levels, seasonal trends, and regional buying behaviors.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain

- Maintenance Manual Generation: Automatically produces technical manuals and how-to guides for machinery maintenance based on real-time IoT data.
- Predictive Maintenance Reports: Summarizes sensor data and predictive analytics into actionable maintenance recommendations, reducing downtime.
- Logistics Optimization Messaging: Crafts communications and insights for supply chain adjustments, shipping delays, and demand variability, enabling quick and informed decisions.
Education

- AI-Curated Study Materials: Generates custom study guides, summaries, and concept maps based on curriculum needs and student performance.
- Personalized Learning Journeys: Designs adaptive learning pathways for individual students based on strengths, weaknesses, and learning style preferences.
- Automated Assessment and Feedback: Grades assignments, provides contextual feedback, and offers suggestions for improvement in real-time.
Legal and Compliance

- Contract Drafting and Review: Assists legal professionals by auto-generating contract drafts and identifying inconsistencies or risk clauses.
- Regulatory Change Summarization: Tracks and summarizes changes in laws or regulations relevant to the organization, ensuring compliance.
- Risk Assessment Scenarios: Uses generative simulations to model legal and compliance risks, supporting better-informed decision-making.
Now, let us check with detail the Generative AI capabilities.
GenAI Capabilities Enabling These Use Cases
a. Interpreting Structured + Unstructured Data
Generative AI models are particularly powerful in handling diverse data sources. Whether it’s structured formats like spreadsheets or databases, or unstructured inputs like handwritten notes, PDFs, or transcriptions, GenAI can synthesize this data into coherent outputs. For industries like healthcare and legal, this means automatically extracting relevant facts from EMRs, policies, or contracts streamlining analysis, reporting, and recommendations.
b. Natural Language Understanding & Generation
At the heart of GenAI is the ability to understand context, intent, and semantics in natural language. This enables it to not only comprehend complex queries or source materials but also generate human-like responses or narratives. In customer support or education, for example, GenAI can produce context-aware responses or personalized tutoring sessions with high relevance and fluency.
c. Real-Time Adaptation Based on Input Context
Generative models excel in dynamically adapting their output to new or evolving inputs. In personalized care or investment advisory, this means adjusting recommendations as user data changes. Real-time input feedback whether from IoT devices or user behavior can trigger new content generation, ensuring outputs remain relevant and timely.
d. Visual + Text + Audio Synthesis
Modern GenAI models are multimodal, capable of synthesizing across text, image, and audio. This enables powerful use cases like creating instructional videos from text, auto-generating product visuals with descriptions, or summarizing spoken content in written form. These capabilities enhance accessibility, learning, and engagement across touchpoints.
Best Practices for Implementation
1. Industry-Specific Readiness Factors
Before diving into GenAI adoption, it is critical for organizations to assess their industry’s level of AI maturity and readiness. This includes evaluating data availability, data quality, regulatory constraints, workforce capability, and digital infrastructure. For example, industries like finance and healthcare operate under strict data governance policies such as HIPAA or GDPR, and therefore require more rigorous planning and safeguards. Conversely, industries like retail or media may have more flexibility to experiment with GenAI use cases due to fewer compliance barriers.
Organizations should also identify where GenAI will deliver the most strategic value: customer experience, operational efficiency, innovation, or a mix of these. Starting with well-scoped pilot projects that align to business KPIs can help demonstrate value and earn stakeholder buy-in for broader implementation.
2. Human-in-the-Loop Design
Generative AI excels at scale, but ensuring human oversight remains crucial especially for sensitive tasks. A “human-in-the-loop” approach ensures outputs generated by AI are reviewed, validated, and refined by domain experts. This not only mitigates risk but enhances trust, accuracy, and accountability.
Use cases such as legal document drafting, patient care plan generation, or financial advisory all benefit from collaborative workflows where humans supervise, correct, or customize the AI’s suggestions. Feedback gathered from human reviewers can be used to further fine-tune the model, improving future outputs.
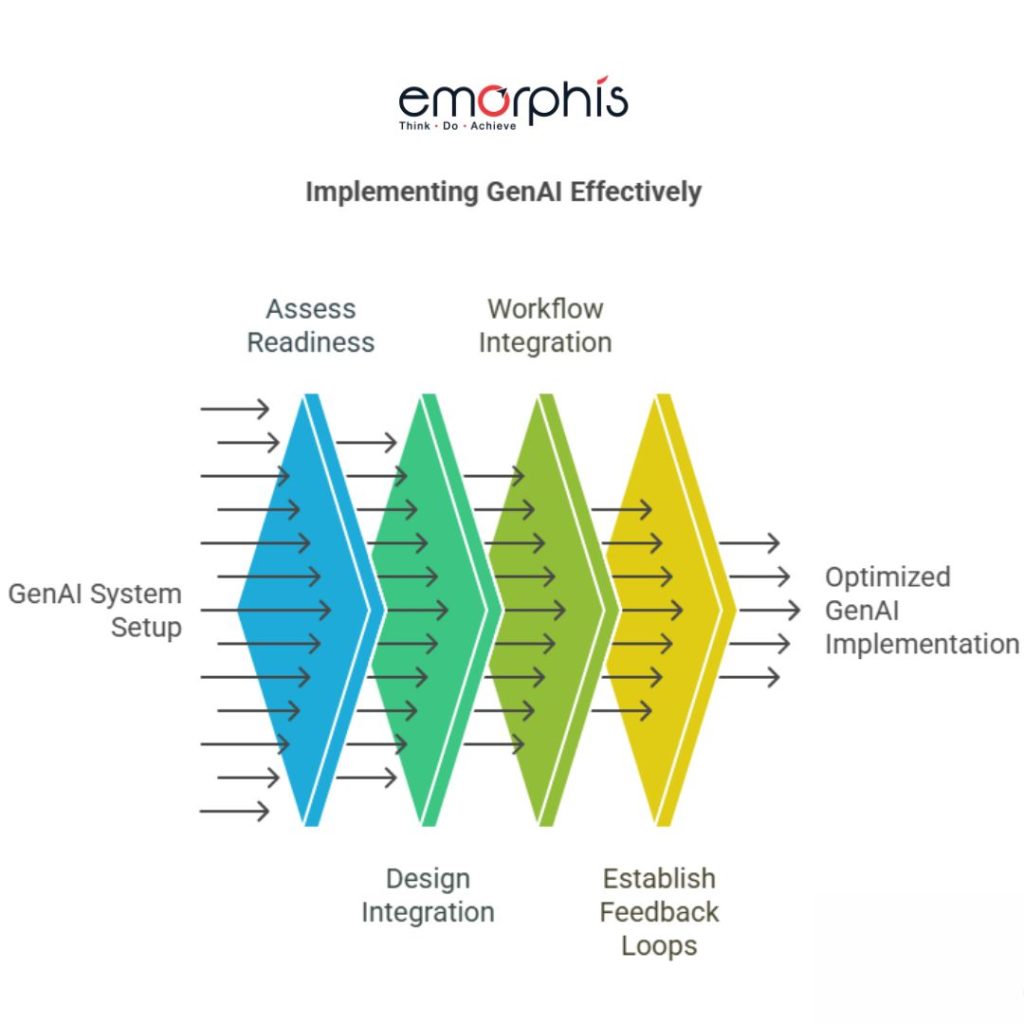
3. Integrating GenAI into Existing Workflows
Rather than building completely new systems, organizations should seek to embed GenAI into existing enterprise tools like CRMs, EMRs, ERP systems, and content management systems. Seamless integration allows teams to adopt GenAI capabilities with minimal disruption and maximizes ROI.
This may include using APIs, no-code AI interfaces, or embedding GenAI outputs into dashboards and reporting tools. Cross-functional collaboration between IT, data science, and business teams is vital to ensure integrations meet user needs and organizational standards.
4. Monitoring and Feedback Loops
Once deployed, GenAI tools should be actively monitored to evaluate performance, accuracy, and alignment with business goals. Establishing metrics such as response quality, user satisfaction, reduction in manual effort, or improved turnaround times can help quantify success.
Regular feedback loops both from users and performance data enable continuous learning and model refinement. Governance frameworks must also be in place to audit decisions, address bias, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. Documentation of AI behavior, version control, and change management becomes essential for maintaining control over GenAI systems in production.
Market Trends and What’s Next
i. Adoption Stats by Industry
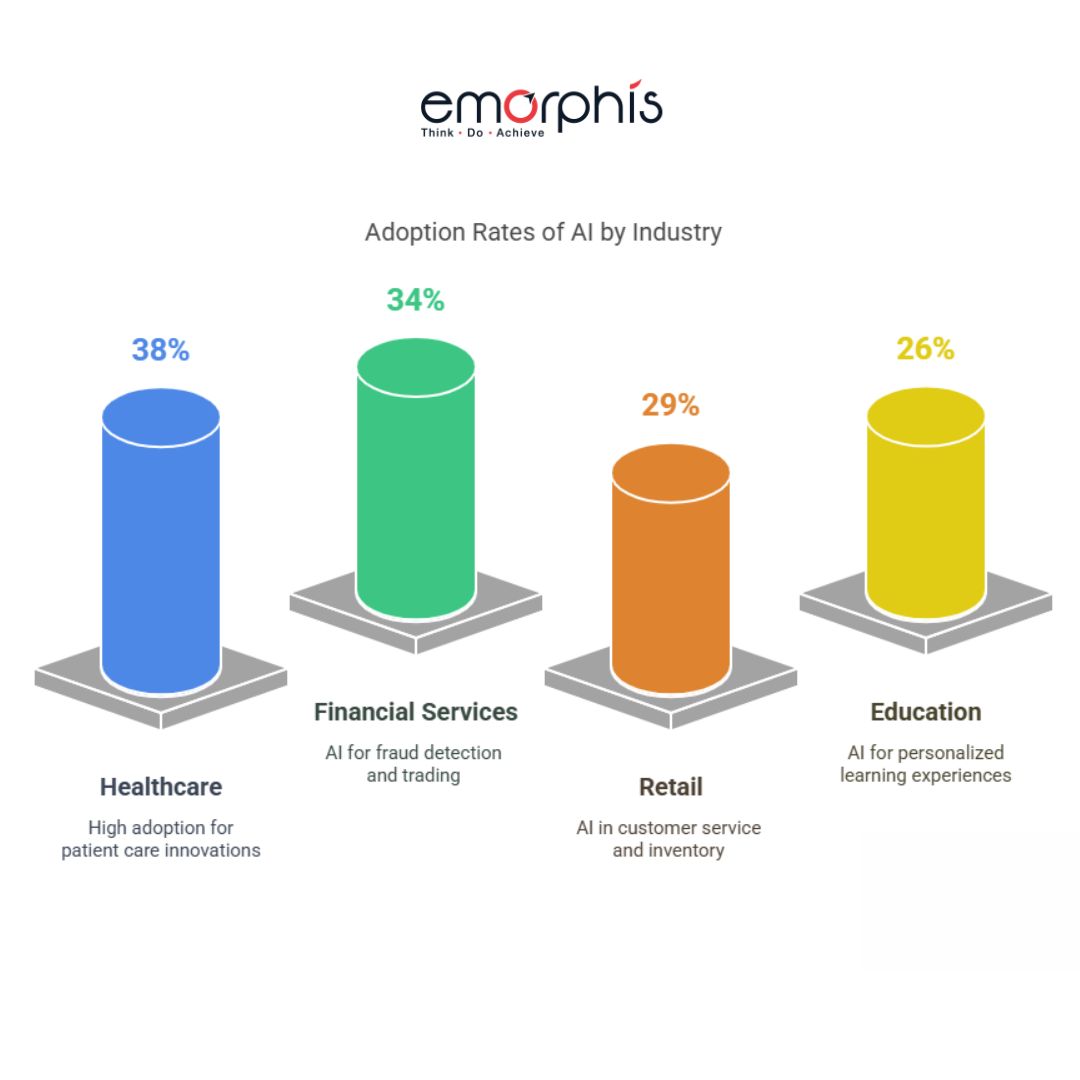
GenAI adoption is accelerating across sectors, driven by strong returns on early investments. As of late 2024, surveys indicate adoption rates of over 38% in healthcare, 34% in financial services, 29% in retail, and 26% in education. These sectors have been quick to implement GenAI due to their large volumes of data and knowledge-intensive workflows.
The trend shows that what began as experimentation is evolving into scaled enterprise deployment. Many organizations are now integrating GenAI into their core platforms, leveraging fine-tuned models to support daily operations, improve productivity, and enhance customer experiences. Larger enterprises are even building proprietary large language models tailored to their specific domain needs.
ii. Future Use Cases Emerging with Multimodal AI
The next wave of generative AI lies in multimodal capabilities—systems that can understand and generate text, images, audio, and video in unified contexts. For example, a healthcare AI assistant might review a patient’s radiology scan, read clinical notes, and verbally communicate diagnostic suggestions. In manufacturing, GenAI could generate 3D visualizations from design briefs while providing textual specifications and cost estimates.
Multimodal AI is also enabling deeper levels of personalization and interaction, such as AI tutors that blend video, speech, and text to create immersive learning environments, or customer support bots that offer voice responses based on real-time emotional analysis.
iii. Regulatory Landscape Evolution
As adoption grows, so does regulatory scrutiny. Governments and international bodies are working on frameworks to ensure responsible AI deployment. Key areas of concern include data privacy, transparency of AI decisions, bias in AI outputs, intellectual property of generated content, and accountability.
Regulations like the EU AI Act and updates to HIPAA and GDPR reflect a shift toward stricter oversight. Enterprises must stay informed of regulatory developments and build AI governance structures that ensure ethical use, compliance, and clear documentation of how generative systems make decisions.
Anticipating and addressing these challenges proactively will be key to sustaining long-term, trust-based use of GenAI across industries.
Conclusion
Generative AI as a Strategic Advantage, GenAI is not just a technological innovation it’s a strategic asset. Organizations leveraging it effectively are outpacing competitors in efficiency, personalization, and innovation. Whether it’s through content automation or intelligent decision-making, the return on investment is tangible and growing.

Building for scalability, trust, and real impact, to fully harness GenAI’s power, organizations must prioritize scalability, governance, and ethical design. Implementing a responsible AI framework, investing in explainability, and aligning use cases with business goals will ensure that GenAI becomes a trusted engine of growth and transformation.
To turn these principles into practical, high-impact solutions, connect with our AI software development experts. Whether you’re just starting your GenAI journey or looking to scale responsibly, our team is here to help you design, build, and deploy AI systems that align with your business goals securely, ethically, and at scale.
Let’s bring your vision to life with innovation you can trust.







