Introduction to Cloud Security Assessment
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses manage and store their data, offering unprecedented flexibility and scalability. However, with this convenience comes the responsibility to ensure the security of sensitive information. Cloud security assessment is a vital process that helps organizations identify potential vulnerabilities, assess risks, and also implement robust security measures to protect their valuable assets.
Understanding the Cloud Security Landscape
Before delving into the details of cloud security assessment, it is essential to grasp the broader cloud security landscape. Cloud environments are complex and dynamic, comprising various service models, such as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS). Additionally, cloud deployments can be public, private, or hybrid, each with its unique security considerations.
Key Components of Cloud Security Assessment
1. Risk Identification
The first step in cloud security assessment involves identifying potential risks associated with the cloud environment. Moreover, this process entails evaluating data exposure, access control mechanisms, authentication protocols, and potential vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure.
2. Compliance and Legal Considerations
Transitioning to the cloud means complying with various industry regulations and legal requirements. Cloud security assessment must include a thorough review of data governance, privacy policies, and also adherence to regional data protection laws.
3. Data Encryption and Storage Security
Transitioning sensitive data to the cloud demands robust encryption and secure storage practices. Assessing the encryption protocols used to safeguard data during transmission and storage is a critical component of cloud security assessment.
4. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Effective IAM is vital in preventing unauthorized access to cloud resources. Evaluating IAM policies, multi-factor authentication, and also access controls is crucial to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data and resources.
5. Incident Response and Recovery
Despite robust preventive measures, security incidents may still occur. Assessing the incident response and recovery plans of cloud service providers is crucial to minimize the impact of potential breaches and also ensure swift recovery.
6. Network Security
Cloud environments rely heavily on network connectivity. Assessing network security includes evaluating firewall configurations, network segmentation, and also monitoring mechanisms to detect and prevent unauthorized network access.
7. Third-Party Vendor Management
Many organizations rely on third-party vendors for cloud services. Evaluating the security practices and track record of these vendors is essential to understand the potential risks they may introduce to the overall cloud security posture.
8. Ongoing Monitoring and Auditing
Cloud security is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Regular monitoring and auditing of cloud resources help identify and as a matter of fact, address emerging security threats and vulnerabilities.
Cloud security assessment plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive data and moreover ensuring the integrity of cloud environments.
In fact, by comprehensively evaluating risks, compliance, encryption practices, access management, incident response, network security, vendor management, and continuous monitoring, organizations can strengthen their cloud security posture and confidently embrace the benefits of cloud computing.
Now, let us check the advantages of cloud security assessments.
Benefits of Conducting Cloud Security Assessments
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, where data breaches and cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, conducting regular cloud security assessments is a proactive and also strategic approach that offers numerous benefits to organizations.
A. Risk Mitigation
Conducting cloud security assessments enables organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities and moreover risks in their cloud environments. By proactively addressing these weaknesses, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of security breaches, data leaks, and unauthorized access.
B. Enhanced Data Protection
Cloud security assessments help organizations understand the security measures in place to protect their data. By evaluating data encryption, storage practices, and access controls, they can ensure that sensitive information is adequately protected, both in transit and at rest.
C. Regulatory Compliance
In today's regulatory landscape, adherence to data protection laws and industry regulations is paramount. Moreover, cloud security assessments ensure that an organization's cloud infrastructure and practices comply with relevant standards, helping them avoid costly fines and legal consequences.
D. Cost-Effectiveness
Identifying and rectifying security issues early on through cloud security assessments can save organizations from potentially huge financial losses, in fact, resulting from data breaches or downtime. The investment in security assessment is significantly smaller than the potential costs of dealing with a security incident.
E. Improved Incident Response
By assessing incident response plans and protocols, organizations can strengthen their ability to detect and also respond to security incidents swiftly and effectively. This leads to faster recovery and minimizes the impact of potential breaches.
F. Vendor Risk Management
For organizations using cloud service providers, cloud security assessments provide insights into the security practices of third-party vendors. In fact, this knowledge empowers organizations to choose reliable and secure partners for their cloud services.
G. Reputation and Trust Building
A strong commitment to cloud security through regular assessments demonstrates to customers, partners, and also stakeholders that an organization takes data protection seriously. This enhances their reputation and builds trust, a crucial factor in today's competitive business landscape.
H. Scalability and Flexibility
As organizations grow and adapt, their cloud environments evolve too. In fact, conducting regular cloud security assessments ensures that security measures keep pace with changing requirements, making cloud adoption more scalable and flexible.
I. Confidentiality and Intellectual Property Protection
Assessing access controls and data encryption measures helps protect an organization's intellectual property and also confidential information from unauthorized access, ensuring a competitive edge and safeguarding valuable assets.
J. Continuous Improvement
Cloud security assessments are not one-off exercises. In fact, they facilitate a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging organizations to stay vigilant and up-to-date with evolving security threats and best practices.
As a matter of fact, conducting cloud security assessments is essential for organizations to protect their data, mitigate risks, comply with regulations, and build a resilient and secure cloud infrastructure. The benefits of these assessments go beyond financial considerations, encompassing enhanced trust, reputation, and also the ability to adapt to an ever-changing cybersecurity landscape. In fact, by investing in proactive security measures, organizations can embrace the full potential of cloud computing with confidence.
Common Challenges in Cloud Security Assessment
Cloud security assessment is a critical process for organizations aiming to protect their assets in the cloud. However, it comes with common challenges that must be navigated effectively to ensure success.
Firstly, the dynamic nature of cloud environments poses a significant hurdle. Cloud infrastructures are highly scalable, making it challenging to maintain an accurate inventory of assets. In fact, constant changes can introduce new vulnerabilities, and traditional assessment methods may struggle to keep pace.
Secondly, the multi-tenancy model in cloud computing introduces unique security concerns. Shared physical resources raise the risk of data leakage or unauthorized access between tenants. Hence, ensuring proper isolation is essential.
Moreover, the complexity of cloud architecture is challenging. Modern cloud environments involve public, private, and hybrid clouds, also making it difficult to identify security gaps cohesively.
Thirdly, a lack of standardization in cloud security assessment frameworks adds to the challenges. Cloud security lacks widely accepted assessment methodologies, hence leading to inconsistent approaches.
Furthermore, a shortage of skilled personnel and expertise in cloud security is a persistent obstacle. In fact, finding professionals with the necessary expertise can be difficult.
Lastly, cloud service providers may resist sharing detailed security information, raising concerns about proprietary measures.
Overcoming these challenges requires a proactive approach. However, organizations must adapt assessment methodologies to the dynamic cloud environment, ensure isolation between tenants, and account for complex architectures. Standardization efforts should be pursued to establish best practices. Additionally, investing in cloud security training is essential to improve the overall security posture.
By addressing these challenges, organizations can reinforce their cloud security and confidently leverage the benefits of cloud computing while safeguarding their critical assets and data.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Security Assessment Framework?
Choosing the proper cloud security assessment framework is crucial for organizations looking to effectively protect their cloud-based data and also applications. In fact, crafting a well-informed decision necessitates thorough deliberation of multiple elements.
Firstly, the framework's alignment with the organization's objectives and specific needs is vital. In fact, understanding the scope of the assessment, compliance requirements, and security goals ensures that the framework is a good fit.
Secondly, selecting a framework based on widely recognized industry standards and best practices is essential. Frameworks like the Cloud Security Alliance's Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) or NIST's Special Publication 800-53 provide established methodologies and also align with industry guidelines.
Thirdly, the framework's scope and coverage must encompass all relevant aspects of cloud security, including data protection, access controls, encryption, and incident response. A comprehensive framework ensures a thorough assessment.
Fourthly, customization and flexibility are crucial considerations. The chosen framework should be adaptable to the organization's unique cloud environment and risks.
Fifthly, compliance with relevant regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA is paramount, especially for industries handling sensitive data.
Sixthly, evaluating the framework's maturity and community support is essential. A well-established framework with an active user community ensures ongoing development and access to resources.
Seventhly, seamless integration with existing security processes and risk management frameworks reduces redundancy and enhances efficiency.
Eighthly, considering the costs and resources required for implementation and maintenance is crucial to strike a balance between effectiveness and affordability.
Ninthly, regular updates to address emerging threats are vital for the framework's relevance and effectiveness.
Lastly, choosing a framework recognized and accepted by third-party auditors and certification bodies can streamline external audits.
By taking into account these considerations, organizations can confidently select the right cloud security assessment framework to enhance their cloud security and mitigate potential risks effectively.

Steps to Perform a Cloud Security Assessment
Performing a comprehensive cloud security assessment is a crucial process to identify vulnerabilities, evaluate risks, and strengthen the overall security posture of cloud-based assets. To achieve this, organizations can follow a structured approach involving several key steps.
Step 1. Identifying Assets and Resources
To initiate the cloud security assessment process, the initial stage involves the identification of all assets and resources present within the cloud environment. This includes applications, data, virtual machines, storage systems, network components, and any other cloud-related services. Creating an accurate inventory helps in understanding the scope of the assessment and ensures that no critical assets are overlooked.
Step 2. Threat Modeling and Risk Analysis
Once the assets are identified, the next step is to perform a threat modeling exercise. Threat modeling helps in identifying potential security threats and attack vectors specific to the cloud environment. Organizations can then assess the likelihood and potential impact of these threats on their assets. This analysis aids in prioritizing security measures and resource allocation based on the risk level.
Step 3. Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing
Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are crucial steps to evaluate the security posture of cloud assets. It also involves automated tools to identify known vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure and applications. Penetration testing, on the other hand, simulates real-world attacks to identify weaknesses that may not be captured by automated scanning tools. Together, these assessments help organizations identify and remediate security gaps effectively.
Step 4. Analyzing Security Controls and Configurations
The cloud security assessment should involve a thorough analysis of security controls and configurations implemented in the cloud environment. This includes examining access controls, encryption protocols, identity and access management settings, and other security features. Properly configured security controls are essential for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and resources.
Step 5. Incident Response and Disaster Recovery Evaluation
Assessing incident response and disaster recovery capabilities is critical to preparing for and mitigating potential security incidents in the cloud. Organizations should review their incident response plans, communication procedures, and recovery strategies. This evaluation ensures that in the event of a security breach or disruption, the organization can respond promptly and effectively, minimizing the impact on operations.
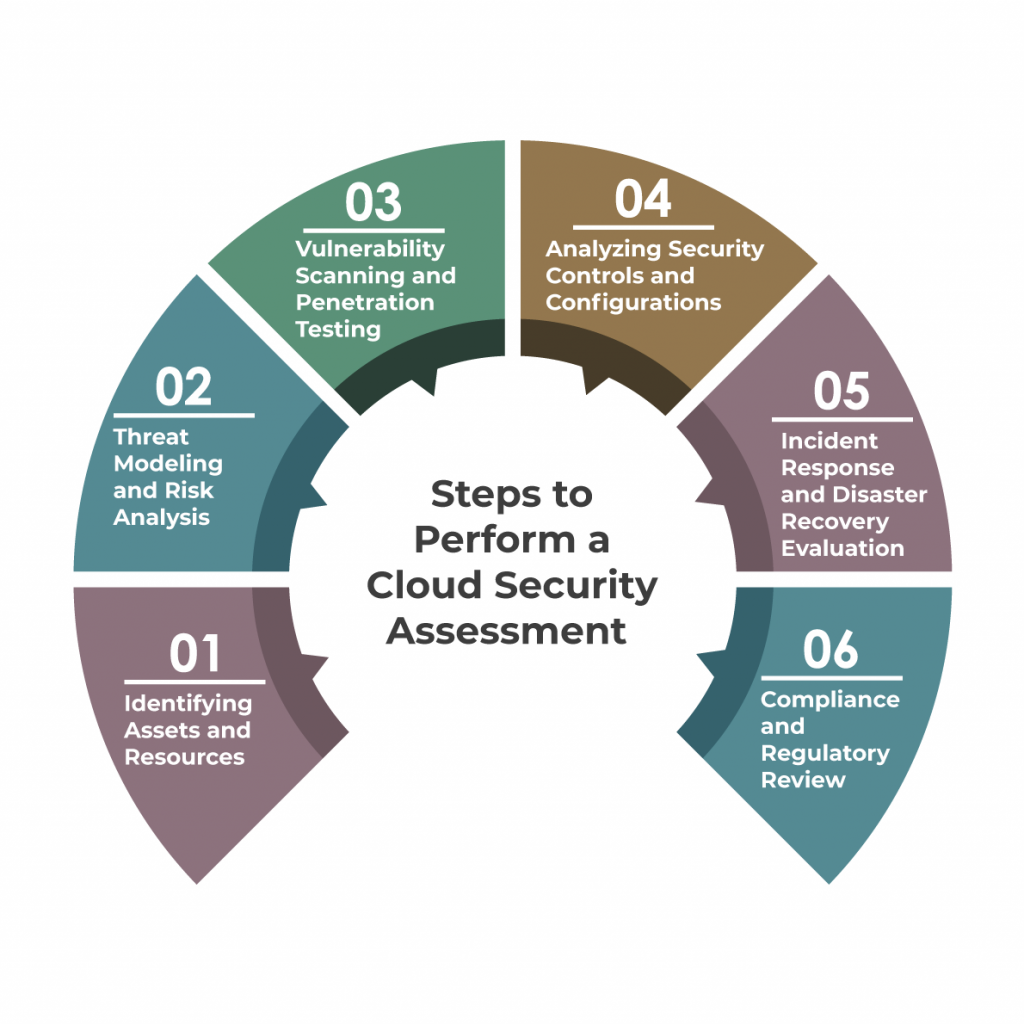
Step 6. Compliance and Regulatory Review
Cloud security assessments should also address compliance requirements and industry regulations relevant to the organization. Reviewing adherence to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 is essential for industries dealing with sensitive data. Organizations should ensure that their cloud practices align with relevant compliance guidelines to avoid potential legal and reputational risks.
A thorough cloud security assessment involves several interconnected steps, starting from identifying assets and resources, performing threat modeling and risk analysis, conducting vulnerability scanning and penetration testing, analyzing security controls and configurations, evaluating incident response and disaster recovery capabilities, and addressing compliance and regulatory requirements. This systematic approach enables organizations to proactively address security vulnerabilities and build a robust cloud security framework to protect their data and applications effectively.
Contact us for Cloud Advisory Services
Best Practices for Cloud Security Assessments
1. Clearly Define the Scope and Objectives
Before conducting a cloud security assessment, it is crucial to define the scope and objectives clearly. This involves identifying the specific cloud assets and services that will be evaluated and understanding the organization's security goals and compliance requirements. A well-defined scope ensures that the assessment focuses on critical areas and avoids unnecessary efforts on irrelevant aspects.
2. Use Reputable and Standardized Frameworks
Leverage reputable and standardized assessment frameworks for the evaluation. Frameworks such as the Cloud Security Alliance's (CSA) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology's (NIST) Special Publication 800-53 offer comprehensive guidelines and align with industry best practices. These frameworks provide a structured approach, ensuring that no critical security aspects are overlooked.
3. Include Technical and Non-Technical Aspects
A comprehensive cloud security assessment should encompass both technical and non-technical aspects. Technical assessments like vulnerability scanning and penetration testing help identify technical vulnerabilities and weaknesses. However, evaluating security policies, procedures, and employee awareness also plays a crucial role in assessing the overall security culture of the organization.
4. Combine Automated and Manual Techniques
The assessment should involve a combination of automated and manual techniques. Automated tools aid in quickly identifying common vulnerabilities and potential misconfigurations. On the other hand, manual analysis allows for a more in-depth investigation of complex security issues that automated tools may not capture. By using both approaches, organizations can achieve a more accurate and comprehensive assessment.
5. Implement Continuous Monitoring and Periodic Assessments
Cloud environments are dynamic and continuously evolving. Implementing continuous monitoring allows organizations to detect and respond to security threats in real time. Regularly scheduled periodic assessments ensure that security measures remain effective and aligned with evolving threats and organizational changes.
6. Involve All Relevant Stakeholders
Cloud security assessments should involve all relevant stakeholders, including IT teams, security experts, and business units. Collaboration among different teams provides diverse perspectives and insights, fostering a more robust security culture within the organization. It also helps in identifying security risks from various angles.
7. Document the Assessment Process and Communicate Findings
Thoroughly document the assessment process to ensure it is repeatable and can be audited in the future. Clear documentation also provides a historical record of the organization's security efforts. Communicating the assessment findings effectively to stakeholders is crucial for decision-making and prioritizing security improvements.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can enhance their cloud security, mitigate potential risks, and ensure the protection of sensitive data and assets in the cloud environment. A systematic and comprehensive approach to cloud security assessments helps in maintaining a strong security posture and staying ahead of emerging threats.

The Future of Cloud Security Assessment
1. Automation and AI Integration
The future of cloud security assessments will witness a significant integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. Automated tools will play a more prominent role in continuous monitoring, threat detection, and vulnerability assessment. AI-driven algorithms will enable faster and more accurate analysis of security data, helping organizations identify and respond to threats in real time. Automated assessments will become more efficient, allowing organizations to detect and mitigate security risks more effectively.
2. Enhanced Threat Intelligence Sharing
Collaboration and threat intelligence sharing among cloud service providers, industry peers, and security communities will be more prevalent in the future of cloud security assessments. Sharing threat intelligence will allow organizations to proactively address emerging threats and vulnerabilities collectively. Cloud security assessment frameworks may incorporate shared threat intelligence to provide more comprehensive risk analysis and assist in identifying new and sophisticated threats.
3. Contextual Risk Assessment
The future of cloud security assessments will shift towards contextual risk assessment. Instead of relying solely on generic risk scores, assessments will consider the specific context of an organization's cloud environment, including its unique threat landscape, industry, and business objectives. This contextual approach will provide more accurate and relevant risk insights, allowing organizations to prioritize security efforts based on their specific risks and business requirements.
4. Cloud-Native Security Solutions
With the increasing adoption of cloud-native technologies, security assessments will evolve to focus on evaluating cloud-native security solutions. Organizations will need to assess the security of serverless computing, containers, microservices, and cloud-native databases. Cloud security frameworks will adapt to address the unique challenges posed by these technologies and ensure that cloud-native applications and services remain secure.
5. Integration of DevSecOps Practices
Cloud security assessments will increasingly integrate with DevSecOps practices in the future. DevSecOps also brings security considerations early into the software development lifecycle, and security assessments will be integrated into the continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. In fact, this integration enables automated security checks at every stage of application development and deployment, fostering a culture of continuous security improvement.
6. Zero-Trust and Identity-Centric Approaches
The future of cloud security assessments will embrace zero-trust and identity-centric security models. Traditional perimeter-based security will be supplemented with granular access controls and also strong authentication mechanisms. In fact, assessments will focus on identity and access management (IAM) practices to ensure only authorized users can access cloud resources, and trust will not be automatically granted based on network location.
7. Compliance Automation and Assurance
Automation will streamline compliance assessments in the future, making it easier for organizations to meet regulatory requirements. Cloud security assessment frameworks will include automated compliance checks, reducing manual effort and human errors in compliance reporting. Automated compliance assurance will ensure that cloud environments consistently adhere to relevant industry standards and regulations.
8. Quantum-Resistant Encryption and Post-Quantum Security
As quantum computing advances, cloud security assessments will incorporate quantum-resistant encryption and post-quantum security measures to safeguard against quantum-based attacks. Preparing for the post-quantum era will become an essential aspect of cloud security assessments to ensure the long-term security of sensitive data and communications.
Before you go recommend checking our Cloud Computing Services
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of cloud security assessment will be characterized by increased automation, AI integration, enhanced threat intelligence sharing, contextual risk assessment, focus on cloud-native technologies, integration with DevSecOps practices, adoption of zero-trust approaches, compliance automation, and preparation for quantum-resistant security.
As cloud technology evolves, these trends will play a vital role in enabling organizations to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities and maintain a strong security posture in the dynamic cloud environment.







