Modern medical systems are nowadays based on the easy access and real-time processing of a great amount of data and medical information characterized by certain grades and types of structuring. Understanding the major importance that eHealth technologies, and electronic database systems have for medical informatics systems led to their quick worldwide adoption, the concept of electronic database evidence has suffered many transformations and reconsiderations along with the increase in complexity and with the change of medical data, simultaneous with health care systems evolution. The sharing of patient information between healthcare organizations and IT systems is changing from a “point to point” model to a “many to many” one.
According to the ISO/TR 20514 definition, using the abbreviation EHR:
“Collection of computerized information referring to the health state of a certain subject stored and transmitted in complete safety, accessible to any authorized user. It has a logic pattern for information organization implemented, universally accepted, and independent from the system. Its main aim is to ensure continuous, efficient, and quality integrated health services along with retrospective and prospective information “.
What is electronic health record (EHR)?
An electronic health record (EHR) is an evolving concept defined as a systematic collection of electronic health information about individual patients or populations. It is a record in digital format that is theoretically capable of being shared across different healthcare settings. In some cases, this sharing can occur by way of network-connected enterprise-wide information systems and other information networks or exchanges. EHRs may include a range of data, including demographics, medical history, medication and allergies, immunization status, laboratory test results, radiology images, vital signs, personal stats like age and weight, and billing information.
Among other types of data, an EHR typically includes:
- Contact information.
- Information about visits to health care professionals.
- Allergies.
- Insurance information.
- Family history.
- Immunization status.
- Information about any conditions or diseases.
- A list of medications.
- Records of hospitalization.
- Information about any surgeries or procedures performed.
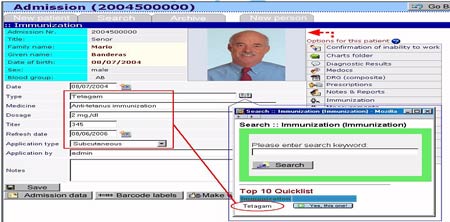 |
| A Standard EHR Preview |
The variations in terminology, often implying the national characteristic, are not only connected to formulation but also to the content and clinical context. Nowadays this concept has many forms for eHealth Technologies:
- EHR/EHCR (electronic healthcare record)
- PCR (patient-carried record)
- CMR (computerized medical record)
- CPR (computer-based patient record)
- EPR (electronic patient record)
- EMR (electronic medical record)
- PHR (personal health record)
Types of data stored in an electronic medical record
An electronic medical record might include:
- Patient demographics.
- Medical history, examination, and progress reports of health and illnesses.
- Medicine and allergy lists, and immunization status.
- Laboratory test results.
- Radiology images (X-rays, CTs, MRIs, etc.)
- Photographs, from endoscopy laparoscopy, or clinical
- photographs.
- Medication information, including side effects and interactions.
- Evidence-based recommendations for specific medical conditions
- A record of appointments and other reminders.
- Billing records.
- Eligibility
- Advanced directives, living wills, and health powers of attorney
What is the business of EMR?
The following three stages of economic return help to decide whether there is a business case for a particular electronic medical records system.
The first stage is characterized by operational efficiencies and workflow automation achieved through process re-engineering and faster access to accurate information. The benefits gained in this stage include reduced overhead costs and professional liability rate reduction.
In the second stage, benefits are derived from increased clinic productivity and decision support at the point of care. As more information is entered into the EMR, standard care protocols, order management, and outcomes analyses can be supported. EMR customers experience quality improvements, compliance with regulatory requirements, and reduced exposure to risk.
Thirdly the longer term, investments in EMR software systems can provide healthcare organizations with a distinct competitive advantage. Looking forward, physicians should anticipate using an electronic medical records system as a tool to manage the business of delivering care efficiently and cost-effectively and to provide more responsive care to an increasingly selective consumer.
Social Benefits:-
- Decreased probability of unnecessary treatments and tests.
- Digitizing medical records can save lives as well by catching Prescription errors like misdosing and drug-drug interactions.
- Electronic medical record improves medical services by making them faster and patients have less stress. Doctors can make prescriptions appointments and referrals at the same time through the digital EMR.
- EMR may help patients to get access to personal health records conveniently on workstations and even on mobile Phones too.
Business Benefits:-
- EMR can cut down the cost by reducing paperwork.
- Data can be very well protected with the EMR.
- Up-to-date record maintenance is easier with the use of EMR.
Important Information Requirements
Physicians: Diagnoses and treatments
Patients: Personal information and a full medical history
Hospital: Prescription medications and the effect of those treatments
Ideal characteristics of an electronic health record (EHR)
- Information should be able to be continuously updated.
- The data existing in an electronic health record system should be able to be used anonymously for statistical reporting, for purposes of quality improvement, outcome reporting, resource management, and public health communicable disease surveillance.
- The ability to exchange records between different electronic health records systems (“interoperability”) would help develop a network between healthcare deliveries in non-affiliated healthcare facilities.
Interoperability
In healthcare, interoperability refers to the ability of different information, technology systems, and software applications to communicate, to exchange data between them, accurately, and effectively, and especially to use the information that has been exchanged.
Organizations to evaluate standardization proposals
- CHI (Consolidated Health Informatics Initiative) – recommends nationwide federal adoption of EHR standards in the United States
- CCHIT (Certification Commission for Healthcare Information Technology) – a federally funded, not-for-profit organization that evaluates and develops the certification for EHRs and interoperable EHR networks (USA)
- IHE(Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise) – a consortium, sponsored by the HIMSS, that recommends integration of EHR data communicated using the HL7 and DICOM protocols
- Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society(HIMSS)– an international trade organization of health informatics technology providers
- American Society for Testing and Materials – a consortium of scientists and engineers that recommends international standards
The benefits of EHRs include
- The ability to automatically share and update information among different offices and organizations.
- More efficient storage and retrieval.
- The ability to share multimedia information, such as medical imaging results, among locations.
- The ability to link records to sources of relevant and current research.
- Easier standardization of services and patient care.
- Provision of decision support systems (DSS) for healthcare professionals.
- Less redundancy of effort.
- Lower cost to the medical system once implementation is complete.
About Emorphis
Emorphis is a global leader in providing software product and application engineering services to Independent Software Vendors (ISVs), software-enabled enterprises, and firms specializing in embedded software solutions. Our eHealth technologies services help clients choose to partner with us to attain their business objectives.
Emorphis is a niche technology firm equipped with extensive experience in eHealth technologies and proficiency across various technology platforms, including .Net, J2EE, PHP, iOS, Android, and Cloud Computing platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS). We specialize in Software QA and Testing, encompassing both manual and automation testing methodologies. Our product designs are tailored to be cloud-ready, and deployable on leading cloud infrastructures like AWS and Azure.
Find the Portfolio for case studies on various eHealth technologies.
Our commitment to engineering innovation and ongoing research and development endeavors enables us to expedite time-to-market, ensure superior quality at cost-effective rates, and foster innovation to stay competitive in the global arena. We prioritize translating your concepts and requirements into impeccably executed solutions. Moreover, we assume end-to-end responsibility for the design, development, and deployment of your product or application.
Specializing in Software Product Engineering, eHealth technologies and Enterprise Mobility Strategies and Implementation, M2M-connected systems development, and Mobile Application development across various platforms including iPhone, Android, BlackBerry, Windows Mobile, Symbian, QT, and J2ME, we are dedicated to delivering cutting-edge eHealth technologies and solutions tailored to meet your specific needs.
Find details of Product Conceptualization